Introduction: Mastering Cab Booking System Design
Cab booking systems, epitomized by Uber, have revolutionized urban transportation. These platforms offer a seamless blend of technology and convenience, enabling users to summon a ride with just a few taps on their smartphones. At the heart of their success lies a sophisticated system design that handles millions of simultaneous users while maintaining a smooth and intuitive user experience.
This guide delves into the core aspects of designing a cab booking system like Uber, focusing on scalability, cost-effectiveness, and diverse ride options. These elements are critical in ensuring the system remains functional and efficient, even as it scales to accommodate more users and diverse needs.
Explore the world of machine learning: Deep Dive into LSTM Networks.
Core Requirements of a Scalable Cab Booking System
High Availability and User Support
Supporting a large user base, such as 100,000 active users, demands robust infrastructure and efficient data-handling strategies. This section will explore how to scale your system to handle such a load without compromising on performance or user experience.
Importance of System Scalability and Reliability
The growth trajectory of a cab booking platform is unpredictable, and the system must be designed to handle sudden surges in demand. Scalability and reliability are not just features but necessities in this landscape.
Efficiency in Booking: Time and Cost Optimization
Techniques to Minimize Booking Time and Cost
Minimizing the time and cost associated with booking a ride is pivotal for user retention. You should examine algorithms and strategies that make the booking process as quick and cost-effective as possible.
Balancing Speed and Efficiency with User Experience
Creating a balance between the system’s speed, efficiency, and overall user experience is a delicate art. This part will cover how to optimize this balance to ensure user satisfaction.
Tidbit:
Did you know? Uber’s system handles over 15 million trips each day, showcasing the massive scale at which cab booking systems operate.
Unlock the power of Hadoop: Beginner’s Guide to the Hadoop Ecosystem.
System Architecture: Designing for Scale and Flexibility
High-Level System Diagram
Creating a Diagram to Visualize Architecture
A high-level system diagram is crucial for visualizing the structure and flow of a cab booking system. This diagram serves as a blueprint, detailing how different components like user interface, server, database, and external APIs interact.
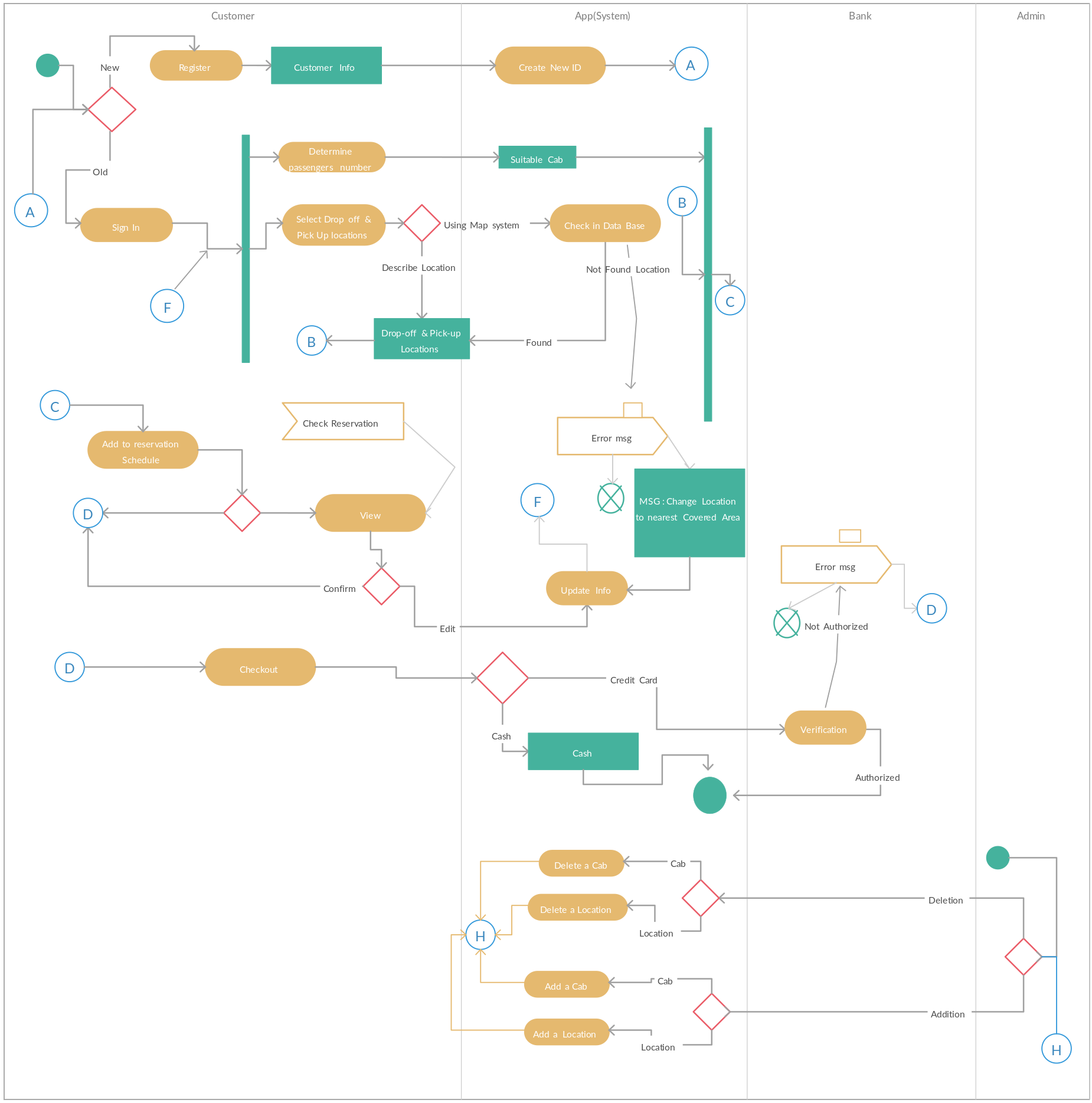
Figure 1: Cab Booking System Blueprint. Source: https://creately.com/diagram/example/ihbyd6t71/cab-booking-system-classic
Tools for System Diagramming
Several tools are available to aid in creating detailed system diagrams. From open-source options like Draw.io to professional tools like Lucidchart and Microsoft Visio.
Addressing Scalability and High Availability
Discussing Design Decisions for Scalability
Designing for scalability involves making key decisions around database management, server architecture, and caching strategies. It would be best if you explored how these decisions impact the system’s growth ability without performance degradation.
Technologies and Tools for Handling High User Load
Handling a high user load requires robust technologies and tools. It would be best if you looked at different databases like MySQL and NoSQL options, server technologies like Node.js, and load balancing techniques that ensure smooth operation under heavy load.
Empower your database knowledge: The Importance of B&B Trees in Indexing.
Advanced Features and User Options
Integrating Diverse Ride Options
Implementing Shared, Dedicated, and Timed Rides
To cater to a broad spectrum of users, a cab booking system must offer a variety of ride options. Shared rides appeal to cost-conscious users, dedicated rides to those seeking privacy, and timed rides for scheduling convenience.
User Interface Considerations for Ride Selection
The user interface (UI) plays a pivotal role in how users interact with these ride options. It should be intuitive, informative, and engaging. This section will cover UI design principles to enhance user experience during ride selection.
Customizing User Experience
Personalization and User Preference Settings
Personalization is key in today’s digital age. By allowing users to set preferences for ride types, pickup locations, and favorite destinations, the system can offer a more tailored experience. We’ll discuss the backend logic and data handling needed for these features.
Impact on System Design and Functionality
Customization options significantly affect the system’s design and functionality. From database schema to API design, every element must be geared towards supporting a flexible and personalized user experience.
Table: Comparison of Ride Options
| Ride Option | Target Audience | Key Feature |
| Shared Ride | Budget-conscious users | Cost-effective, eco-friendly |
| Dedicated Ride | Privacy-seeking users | Exclusive use of the vehicle |
| Timed Ride | Schedule-oriented users | Book rides for future times |
What’s your take on system design? Share from System Design Fundamentals.
The Backbone of the System: Backend Development in Detail
Building a Robust Backend
Technologies for Backend Development
The choice of backend technology can significantly impact the performance and scalability of a cab booking system. Let’s consider three popular backend technologies:
1. Node.js:
Ideal for handling concurrent requests due to its non-blocking I/O model. For instance, Node.js can handle user location updates efficiently:
Javascript
app.post(‘/updateLocation’, (req, res) => {
const { userId, location } = req.body;
updateUserLocation(userId, location);
res.send({ status: ‘Location updated’ });
});
This snippet shows a basic Node.js server handling location updates, a frequent operation in cab booking apps.
2. Python with Django or Flask:
Known for its readability and efficiency. Python is great for processing complex algorithms, like fare calculation based on distance and time:
Fare = Base Fare + (Cost per Mile × Distance) + (Cost per Minute × Time)
Python
def calculate_fare(distance, time):
base_fare = 2.50 # Base fare
cost_per_mile = 1.75 # Cost per mile
cost_per_minute = 0.25 # Cost per minute
return base_fare + (cost_per_mile distance) + (cost_per_minute time)
This Python function calculates fare, which is a crucial part of the backend logic.
Ensuring System Resilience and Efficiency
To ensure resilience, we use a microservices architecture. Microservices allow different parts of the application, like user management, payment processing, and ride matching, to operate independently. This separation enhances system resilience as it prevents a failure in one service from impacting others.
Data Handling and Management
Database Design for Scalability
A well-structured database is key for scalability. SQL databases like PostgreSQL are often used for their reliability and ACID compliance. However, for high scalability and flexibility, NoSQL databases like MongoDB are preferred due to their schema-less structure.
Let’s consider a MongoDB schema for storing user data:
Javascript
{
userId: “U123”,
name: “John Doe”,
location: { type: “Point”, coordinates: [-73.856077, 40.848447] },
rideHistory: [{ rideId: “R1”, fare: 25.50, distance: 5.2 }, …]
}
In this schema, `location` is stored as a GeoJSON object, which is efficient for location-based queries crucial in cab booking systems.
Handling Concurrent User Requests
Concurrency is a major challenge. A common strategy is to use a load balancer that distributes incoming requests across multiple servers, ensuring no single server gets overwhelmed.
Consider this mathematical representation of load balancing:
Total Requests per Second = (Requests on Server 1 + Requests on Server 2 + … + Requests on Server N) / Number of Servers
This equation illustrates how the load is distributed evenly across multiple servers, enhancing the system’s ability to handle concurrent requests.
Code Snippet for Load Balancing:
Python
# Python pseudo-code for a simple load balancer
def distribute_load(request, server_list):
selected_server = select_least_loaded_server(server_list)
forward_request_to_server(request, selected_server)
This pseudo-code represents a basic load-balancing mechanism, where requests are forwarded to the least loaded server.
Learn the intricacies of LRU Cache: Deep Dive into LRU Cache.
Front-end Development: Crafting the User Interface
Front-end development in a cab booking system like Uber is all about creating an engaging, intuitive, and responsive interface that resonates with the user’s needs. This section delves into the principles of user interface design, the implementation of interactive features, and the underlying code that brings these elements to life.
Design Principles for User Interface
Ensuring Usability and Accessibility
The key to a successful user interface in cab booking systems lies in its usability and accessibility. The UI should be intuitive, easy to navigate, and accessible to users with diverse abilities.
Consider the following principles:
- Simplicity: Keep the interface clean and uncluttered.
- Consistency: Use consistent elements for navigation and actions.
- Feedback: Provide immediate feedback for user actions, like a visual confirmation after booking a ride.
Responsive Design for Various Devices
Responsive design ensures that the app’s UI looks and functions well on all devices, whether it’s a smartphone, tablet, or desktop. This involves using flexible grid layouts, adaptable images, and media queries in CSS.
For Example, a CSS media query for responsive design:
CSS
@media screen and (max-width: 600px) {
.container {
width: 100%;
}
.navigation {
font-size: 12px;
}
}
This CSS snippet adjusts the layout and font size based on the screen width, enhancing the user experience on smaller devices.
Implementing Interactive Features
Code Snippets for Key Features
Interactive features are what make a cab booking app truly stand out. Let’s look at some examples:
1. Map Integration:
Using APIs like Google Maps for displaying maps and routes. JavaScript snippet for integrating Google Maps:
Javascript
function initMap() {
var map = new google.maps.Map(document.getElementById(‘map’), {
center: {lat: -34.397, lng: 150.644},
zoom: 8
});
}
This code initializes a Google Map centered on a specific location.
2. Live Location Tracking:
Updating the user’s location in real-time is critical for matching them with nearby drivers. JavaScript snippet for tracking user location:
Javascript
navigator.geolocation.watchPosition(function(position) {
updateMapWithCurrentLocation(position.coords.latitude, position.coords.longitude);
});
This JavaScript function tracks the user’s current location and updates the map accordingly.
Explanation of Functionality
Understanding the functionality behind these features is crucial. For Example, the map integration uses the Google Maps API to render maps and calculate routes. The live location tracking utilizes the Geolocation API to get the user’s current location and updates the map in real time.
Table: Front-end Technologies and Their Benefits
| Technology | Benefit | Example Use Case |
| HTML/CSS | Structure and style | Responsive layouts |
| JavaScript | Interactivity | Map integration, live updates |
| React/Angular | Dynamic UI | Single-page applications |
Payment Integration and Optimization
Incorporating a reliable and user-friendly payment system is a cornerstone of any successful cab booking app. This section will cover the essentials of payment integration, focusing on selecting the right payment gateways, ensuring security, and streamlining the payment process for a smooth user experience.
Selecting Payment Gateways
Criteria for Choosing the Right Gateway
Choosing the right payment gateway is crucial for both the security and convenience of transactions. Key factors include:
- Security and Compliance: Ensure the gateway adheres to standards like PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard).
- Transaction Fees: Consider the cost per transaction, as it impacts the overall profitability.
- User Experience: Look for gateways offering a seamless and quick payment process.
Popular payment gateways like Stripe, PayPal, and Braintree each have their strengths and can be integrated using their respective APIs.
Security and Compliance Considerations
It’s imperative to handle user payment information with utmost care. Ensure encryption of payment details and compliance with global security standards.
For instance, Stripe provides a secure way to handle card information:
Javascript
// Example using Stripe Elements for secure card transactions
stripe.createToken(card).then(function(result) {
if (result.error) {
// Inform the user if there was an error
showError(result.error.message);
} else {
// Send the token to your server
processPayment(result.token);
}
});
This JavaScript snippet creates a secure token for the card information, ensuring that sensitive data never touches your server.
Streamlining the Payment Process
Enhancing User Payment Experience
A streamlined payment process reduces friction and enhances user satisfaction. Implementing features like saving card details for future use, offering multiple payment options, and providing clear payment breakdowns are essential.
Code Examples for Payment Integration
Integrating a payment gateway typically involves backend and front-end interactions. Here’s a simplified example using Stripe:
Backend (Node.js): Javascript
app.post(‘/charge’, async (req, res) => {
try {
let {amount, token} = req.body;
let charge = await Stripe.charges.create({
amount: amount,
currency: ‘usd’,
description: ‘Cab fare’,
source: token,
});
res.send(charge);
} catch (error) {
res.send(error);
}
});
This Node.js server endpoint creates a charge using Stripe’s API.
Front-end: Javascript
//code to submit the payment form and token to the server
submitPaymentForm(token) {
fetch(‘/charge’, {
method: ‘POST’,
headers: {‘Content-Type’: ‘application/json’},
body: JSON.stringify({token: token, amount: fareAmount})
}).then(response => response.json())
.then(data => showConfirmation(data));
}
Find passion in web development: Web Development Essentials.
Challenges and Design Decisions
Navigating through the labyrinth of system design for a cab booking app like Uber involves confronting various challenges and making critical design decisions. This section sheds light on these aspects, offering insights into tackling key issues and balancing different factors for optimal performance.
Tackling Key Challenges in System Design
Handling Peak Loads
One of the most daunting challenges is managing peak load times, like during rush hours or special events. Strategies to handle this include dynamic scaling of resources, efficient load balancing, and implementing robust caching mechanisms.
Ensuring Data Consistency
With numerous concurrent transactions, maintaining data consistency is paramount. Techniques like database sharding, using transactional databases, and implementing distributed systems principles are essential.
Design Decisions for Optimal Performance
Trade-offs in Technology Selection
Every technology choice comes with its trade-offs. For instance, choosing a highly scalable NoSQL database might sacrifice some aspects of ACID (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability) compliance inherent in SQL databases.
Balancing Cost, Efficiency, and User Experience
Striking the right balance between cost, system efficiency, and user experience is crucial. Cost-effective cloud solutions can be leveraged for efficiency while ensuring the user interface is responsive and intuitive.
Table: Design Decisions and Challenges
| Challenge | Design Decision | Impact |
| Peak Loads | Dynamic Scaling, Load Balancing | Ensures uninterrupted service |
| Data Consistency | Database Sharding, ACID Compliance | Maintains reliable data transactions |
| Technology Trade-offs | Choice of Database, Backend Tech | Affects scalability, performance |
| Cost-Efficiency Balance | Cloud Solutions, Efficient Algorithms | Impacts overall system sustainability |
Alternative Tools and Technologies
In the realm of cab booking system design, a plethora of tools and technologies exist beyond mainstream choices. This exploration will illuminate some alternative options, discussing their advantages and disadvantages and how they can adapt to evolving technological trends.
Exploring Different Tech Stacks
Overview of Alternate Technologies and Tools
Diverse tech stacks offer different benefits for cab booking systems. For instance:
- Elixir and Phoenix: Known for handling high concurrency, these are great for real-time features like ride tracking.
- Go (Golang): Offers excellent performance and is efficient in handling large numbers of requests, suitable for the backend.
- js: A progressive JavaScript framework that can be used to build more maintainable and testable front-end code.
Pros and Cons of Different Approaches
Each technology comes with its set of pros and cons:
- Elixir/Phoenix: Pro – High concurrency; Con – Smaller community and ecosystem.
- Go: Pro – High performance; Con – Less expressive than languages like Python.
- js: Pro – Easy integration; Con – Less widespread use compared to React or Angular.
Adapting to Changing Technological Trends
Keeping the System Flexible for Future Updates
The technology landscape is constantly evolving. It’s essential to design systems that are flexible enough to incorporate new technologies and trends. This involves following best practices like modular design, API-first development, and continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines.
Incorporating Emerging Technologies
Emerging technologies like AI and machine learning can be leveraged for advanced features like predictive ride-matching, dynamic pricing models, and enhanced user experiences. Staying abreast of these developments and thoughtfully integrating them can give a cab booking system a significant edge in the market.
Get to know about Consistent Hashing and Load Balancing at Consistent Hashing and Load Balancing.
Conclusion: Embarking on Your Design Journey
As we culminate this extensive exploration into designing a cab booking system akin to Uber, let’s encapsulate the key insights and strategies that have been illuminated throughout this guide.
The world of system design and development is vast and ever-evolving. This guide provides a foundation, but the real learning comes from experimentation and innovation. You are encouraged to dive deep, experiment with different technologies, and think creatively to solve unique challenges in system design.
Embarking on the journey to design and develop a cab booking system is both challenging and rewarding. It offers a plethora of learning opportunities and the potential to create something impactful. As you step into this realm, remember to embrace the challenges, stay curious, and keep innovating. Your journey in shaping the future of urban mobility starts now!
And with that, we conclude our comprehensive guide on designing and creating a cab booking system like Uber. Whether you’re a novice stepping into the world of development or an experienced programmer looking to expand your skill set, this guide offers valuable insights and practical knowledge to aid you on your journey. Remember, the road to mastery is paved with curiosity, experimentation, and continuous learning. Happy coding, and best of luck in your technological endeavors!
Learn how to live healthily with technology in Principals of Living a Healthy Lifestyle.

Recent Comments